Meson
Meson is a tool that helps with compilation of C/C++ of more than just a few standalone files. We have seen in “Organizing Code in C++” that compiling C++ files is usually done in two stages, the creation of object files and the linking of those objects. Meson will generate these compilation steps for you, provided you give it the right information about your project. In addition, Meson has the following advantages:
- Cross-platform: the workflow to compile Meson project is identical accross platforms, Meson will automatically identify the relevant compilers, dependencies, etc., to use for your particular platform.
- It correctly handles library dependencies: these can be hard to setup manually, especially in high-performance cluster environments.
- Many IDEs recognize Meson projects: among them CLion and VScode.
Adding subdirectories with separate executables
For organizing your milestone codes, it can be useful to have seperate main.cpp files in seperate subdirectories that correspond to each milestone. A possible directory structure could look like this:
milestones/
meson.build
01/
meson.build
main.cpp
...
04/
meson.build
main.cpp
lj54.xyz
...
Each subdirectory contains a meson.build that tells Meson what to do. You can tell Meson to add a subdirectory using the subdir command. The toplevel meson.build requires an additional statement
subdir('milestones')
and meson.build in the milestones subdirectory looks as follows:
subdir('01')
subdir('02')
subdir('03')
...
In each of the milestone directories we need to tell Meson to compile an executable and that main.cpp (in this directory) contains the main function. Additionally, it is useful to tell Meson about dependent files, e.g. the file lj54.xyz that is required to execute Milestone 04. The corresponding meson.build looks like this:
executable(
'milestone04',
'main.cpp',
include_directories : [md_incdirs],
link_with : [md_lib],
dependencies : [eigen, mpi]
)
fs = import('fs')
fs.copyfile('lj54.xyz')
The statement executable contains all source and headers files required to compile the code. The variables eigen and mpi are defined in the toplevel meson.build and can be used here.
In CLion, these additional executables should show up as build targets:
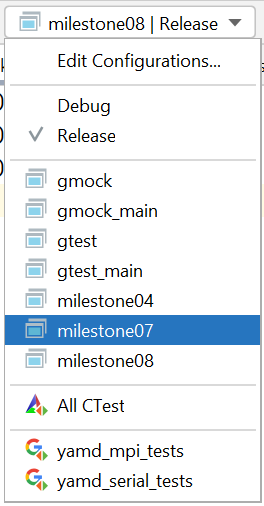
Debug vs. release builds
By default, CLion (and Meson) will configure debug builds. These builds are useful for development purposes, but their performance can be terrible. For running longer calculations it is useful to switch to a release build. This behavior is controlled by the --buildtype= option of the Meson build system. From the command line, it can be set by executing
meson setup builddir --buildtype=debug
In CLion, you can configure this in the menu option File->Settings->Build, Execution, Deployment->Meson. You should see the following dialog:
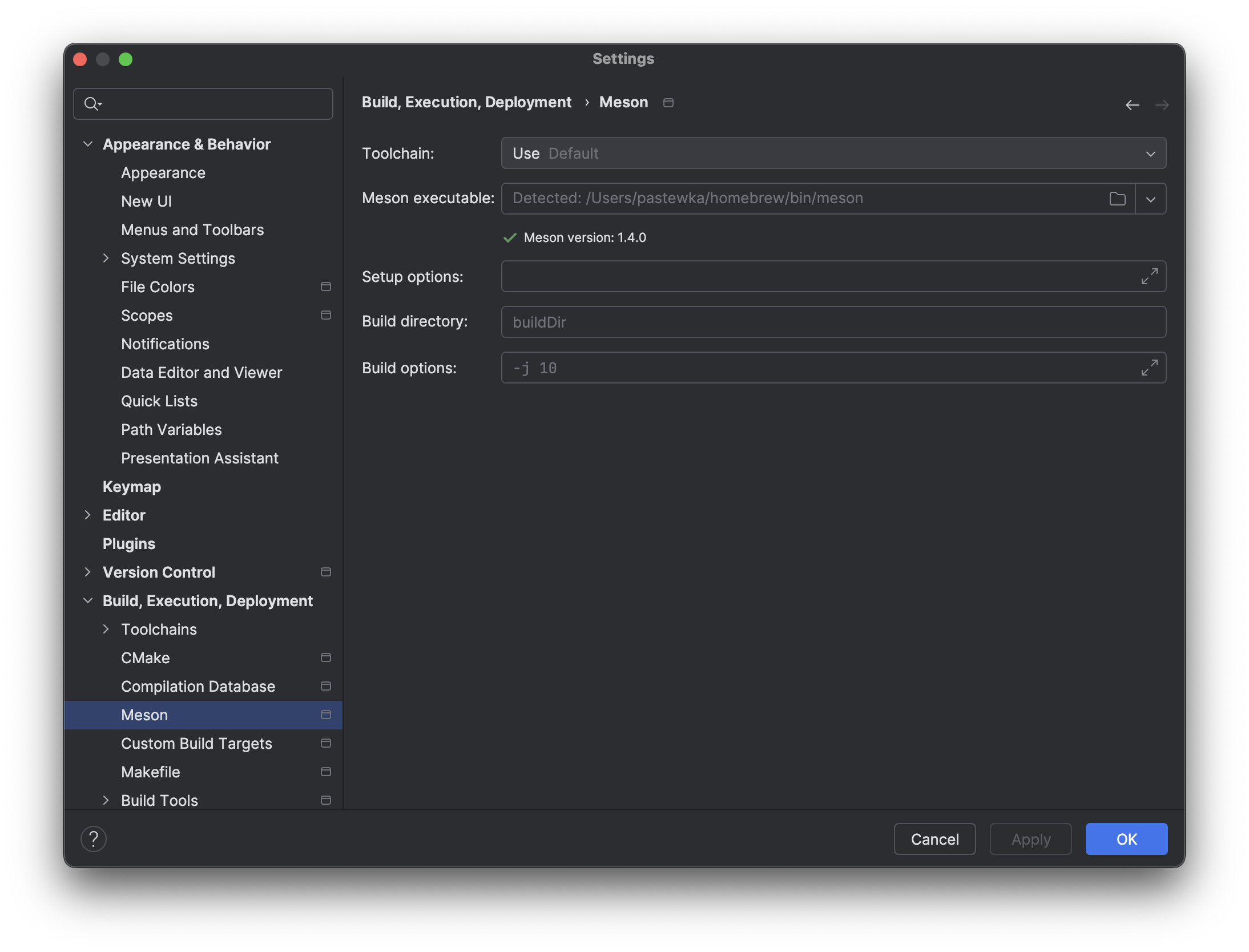
Add the build type to Setup options.